Tue, 25 Feb 2025 09:32:44 +0100

The cavitation process in ultrasonic cleaning is based on fundamental physical principles:
WATCH OUR CAVITATION TEST
What will you see in the video?
At DCM Ultrasonic we did a cavitation test to be able to show you, through a simple and effective method, how to know if your ultrasonic cleaning machine has correct cavitation. For this test, a Pyrex with a very small amount of water inside was used. In the video you can see how the water is atomizing and turning into very small drops of water.
If this phenomenon occurs, it means that your ultrasonic machine is cavitating correctly and the bath is in conditions to clean the parts. If the water does not atomize inside the Pyrex, it means that the machine is not cavitating. Another way to perform this test is to put a thin aluminum sheet inside the Pyrex. Proper cavitation will produce uniform perforations and wrinkles across the entire surface of the sheet.
To ensure the effectiveness of an ultrasonic cleaning machine, it is essential to regularly check the cavitation performance. There are several methods to evaluate this performance:
1. Aluminum Foil Test
This simple method allows the distribution and effectiveness of cavitation to be visualized:
2. Chemical Indicators
Chemical indicators are designed to change color in the presence of effective cavitation:
3. Electronic Measuring Devices
Specialized equipment exists that measures parameters such as acoustic intensity and cavitation distribution:
The effectiveness of cavitation can be influenced by several factors:
1. Ultrasound Frequency
2. Liquid Temperature
3. Composition of the Cleaning Liquid
4. Tank Design and Part Placement
Here are answers to the most common questions regarding cavitation in ultrasonic cleaning:
What types of contaminants can be removed by cavitation?
Cavitation is effective at removing oils, greases, oxides, polishing residues, dust particles, and other contaminants adhering to solid surfaces.
Is ultrasonic cleaning safe for electronic components?
Yes, as long as appropriate frequencies are used and immersion of sensitive components in water is avoided. It is advisable to consult the manufacturer's specifications before proceeding.
How often should I perform cavitation testing on my equipment?
It is recommended to perform cavitation testing at least once a week to ensure optimal equipment performance.
Can I use tap water in my ultrasonic tank?
Although it is possible, using deionized or distilled water with specific additives improves cleaning effectiveness and prevents deposit formation
At DCM Ultrasonic we carry out maintenance and technical assistance for all types of brands and models of ultrasonic cleaning machines, if you need our repair and maintenance services, please contact us.

News
Cavitation and its importance for proper ultrasonic cleaning
25 February de 2025
Cavitation is the fundamental principle that underpins the effectiveness of ultrasonic cleaning machines. This physical phenomenon allows for the removal of contaminants from complex surfaces in an efficient and precise manner. In this article, we will explore in depth what cavitation is, how its effectiveness can be assessed, the factors that affect it, and answer the most frequently asked questions about this process.What is Cavitation?
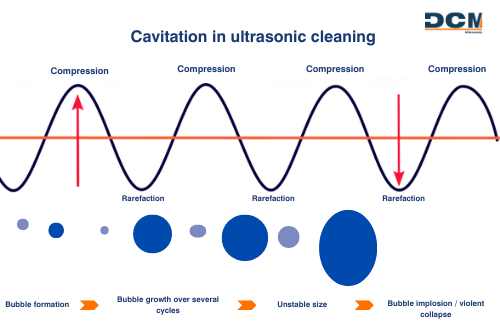
Cavitation is a phenomenon that occurs in liquids when they are subjected to rapid pressure changes, generating the formation and collapse of vapor bubbles. In the context of ultrasonic cleaning, cavitation is induced by high-frequency sound waves that create alternating compression and decompression cycles in the cleaning liquid. During the decompression cycles, microbubbles are formed, which, upon collapsing in the compression cycles, release energy in the form of shock waves and heat. This release of energy produces microjets that impact submerged surfaces, dislodging and removing contaminants even in hard-to-reach areas.
The Science Behind Cavitation
The cavitation process in ultrasonic cleaning is based on fundamental physical principles:
- Sound Wave Generation: Transducers convert electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves, typically between 20 kHz and 100 kHz.
- Microbubble Formation: Sound waves create zones of high and low pressure in the liquid. In low-pressure zones, microbubbles of vapor form.
- Bubble Collapse: During high-pressure phases, these bubbles collapse violently, generating microjets and shock waves.
- Contaminant Removal: The energy released during bubble collapse disintegrates and dislodges contaminants adhering to the surfaces of submerged objects.
WATCH OUR CAVITATION TEST
What will you see in the video?
At DCM Ultrasonic we did a cavitation test to be able to show you, through a simple and effective method, how to know if your ultrasonic cleaning machine has correct cavitation. For this test, a Pyrex with a very small amount of water inside was used. In the video you can see how the water is atomizing and turning into very small drops of water.
If this phenomenon occurs, it means that your ultrasonic machine is cavitating correctly and the bath is in conditions to clean the parts. If the water does not atomize inside the Pyrex, it means that the machine is not cavitating. Another way to perform this test is to put a thin aluminum sheet inside the Pyrex. Proper cavitation will produce uniform perforations and wrinkles across the entire surface of the sheet.
How to Perform a Cavitation Test
To ensure the effectiveness of an ultrasonic cleaning machine, it is essential to regularly check the cavitation performance. There are several methods to evaluate this performance:
1. Aluminum Foil Test
This simple method allows the distribution and effectiveness of cavitation to be visualized:
- Preparation: Cut a thin sheet of aluminum foil that covers the surface of the cleaning tank.
- Immersion: Immerse the foil in the cleaning liquid, making sure it is fully extended and does not touch the walls of the tank.
- Activation: Turn on the ultrasonic equipment and let it run for approximately one minute.
- Inspection: Remove the foil and observe it against the light. Proper cavitation will produce uniform perforations and wrinkles across the entire surface of the foil.
2. Chemical Indicators
Chemical indicators are designed to change color in the presence of effective cavitation:
- Placement: Vials or strips containing a reagent solution are introduced into the cleaning tank.
- Process: When the equipment is activated, cavitation causes a chemical reaction that changes the color of the solution.
- Evaluation: A uniform color change indicates adequate cavitation throughout the tank.
3. Electronic Measuring Devices
Specialized equipment exists that measures parameters such as acoustic intensity and cavitation distribution:
- Sensors: Sensors are placed at different points in the tank to measure the intensity of the ultrasonic waves.
- Data Analysis: The data collected is analyzed to identify variations in cavitation and adjust equipment parameters as needed.

Factors Affecting Cavitation
The effectiveness of cavitation can be influenced by several factors:
1. Ultrasound Frequency
- Low frequencies (20-40 kHz): Generate larger bubbles and more aggressive cleaning, suitable for heavy contaminants.
- High frequencies (40-100 kHz): Produce smaller bubbles, ideal for cleaning delicate components without damaging them.
2. Liquid Temperature
- Optimal Temperatures: Generally between 50°C and 70°C, since increasing the temperature reduces the viscosity of the liquid and improves bubble formation.
- Precautions: Excessively high temperatures can cause evaporation of the liquid and reduce the effectiveness of cavitation.
3. Composition of the Cleaning Liquid
- Additives: The use of specific detergents can improve cavitation effectiveness by reducing the surface tension of the liquid.
- Concentration: Maintaining the proper concentration of additives is crucial to prevent excessive foaming or cavitation reduction.
4. Tank Design and Part Placement
- Tank Geometry: Proper design ensures even distribution of ultrasonic waves.
- Part Positioning: Parts should not touch the tank walls and should be spaced apart to allow for even cleaning.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cavitation
Here are answers to the most common questions regarding cavitation in ultrasonic cleaning:
What types of contaminants can be removed by cavitation?
Cavitation is effective at removing oils, greases, oxides, polishing residues, dust particles, and other contaminants adhering to solid surfaces.
Is ultrasonic cleaning safe for electronic components?
Yes, as long as appropriate frequencies are used and immersion of sensitive components in water is avoided. It is advisable to consult the manufacturer's specifications before proceeding.
How often should I perform cavitation testing on my equipment?
It is recommended to perform cavitation testing at least once a week to ensure optimal equipment performance.
Can I use tap water in my ultrasonic tank?
Although it is possible, using deionized or distilled water with specific additives improves cleaning effectiveness and prevents deposit formation
At DCM Ultrasonic we carry out maintenance and technical assistance for all types of brands and models of ultrasonic cleaning machines, if you need our repair and maintenance services, please contact us.
